Children with Weakened Left Brain Function are Imaginative and Social, but May Struggle Academically in a Traditional Classroom Environment
 Our brains consist of two sides or hemispheres. Children with behavioral, academic, social, or other challenges often have an imbalance in hemispheric brain communication - what we refer to as functional disconnection syndrome, or where one hemisphere is processing information too slowly. This causes one side of the brain to be stronger, while the other side develops more slowly and is weaker.
Our brains consist of two sides or hemispheres. Children with behavioral, academic, social, or other challenges often have an imbalance in hemispheric brain communication - what we refer to as functional disconnection syndrome, or where one hemisphere is processing information too slowly. This causes one side of the brain to be stronger, while the other side develops more slowly and is weaker.
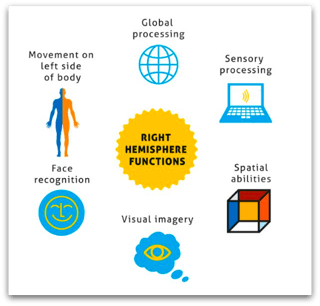
The right hemisphere of the brain controls sensory processing and expression. Children who are left brain weak are often very visual, spontaneous, emotional and intuitive but may struggle academically with memorizing facts and paying attention to details.
Traits of the Right Hemisphere of the Brain
Creative kids tend to be right-brained, and when in learning situations they prefer to:
- Be shown rather than told how to do a task.
- Solve problems by looking at similarities and patterns.
- Draw rather than write.
- Physically handle objects.
- Answer open-ended questions rather than multiple choice tests.
- Discuss topics.
- Assimilate whole chunks of information rather than break them down into discrete facts.
Left Brain Weak Children at School
Modern education systems are developed mainly for left-brained children, who like to structure, plan, work alone, and solve problems with logic. Left brain weak students may find it difficult to settle into school routines and often need assistance in order to cope successfully with the challenges of scholastic life.
You may find that your left-brain weak child has problems with memorizing lists or tables, has difficulty understanding verbal instructions, struggles with writing, cannot focus on one task for too long, and generally doesn't enjoy school. Dyslexia is also common among right brain dominant children.
Learning Strategies
Because these child can often find it difficult to memorize facts with auditory cues such as repetition or rhymes, a good idea is to provide visual cues like picture stories which appeal to the emotions or concrete objects like blocks or colored counters. For example, when teaching letters of the alphabet or vocabulary, integrate the letter or word into a small cartoon so that your child remembers the whole picture. Use a similar strategy for numbers, bringing colors and images into play.
Working in groups is an ideal situation for left brain weak children as they like to tackle art projects and often come up with stimulating and original ideas. They respond well to visual demonstrations on PowerPoint and enjoy music, videos, and dance as methods of learning. Role playing is enjoyed by right-brainers, as they prefer to be in the middle of the action rather than listening to a lesson.
How to Use This Information to Help Your Child
Because children with weak left brains tend to be disorganized and have difficulty focusing for any length of time, they often don't perform well in school and parents may become discouraged. However, the left side of the brain—which tends to focus on the details of life, is logical, and breaks down problems into solvable pieces—can be brought up to speed.


Contact us today to schedule an assessment. You can also view the research and results of the program on the website.
Enjoy These Articles Related to Brain Function and Development
Characteristics of a Left-Brained Child
Tips for Motivating Right-Brain Children to Learn
How to Inspire Creative Thinking in Left-Brain Dominant Children